Click here and press the right key for the next slide.
(This may not work on mobile or ipad. You can try using chrome or firefox, but even that may fail. Sorry.)
also ...
Press the left key to go backwards (or swipe right)
Press n to toggle whether notes are shown (or add '?notes' to the url before the #)
Press m or double tap to slide thumbnails (menu)
Press ? at any time to show the keyboard shortcuts
The Core Idea

The Core Idea
s.butterfill@warwick.ac.uk & c.sinigaglia
notes on our web page
http://two-systems.sinigaglia.and.butterfill.com/
approximate timing
11.05 -- 11.40 : 35 minutes lecture (ask questions at any point)
11.40 -- 11.55 : 15 minutes discussion
11.55 -- 12.05 : 10 minutes break
12.05 -- 12.40 : 35 minutes lecture (ask questions at any point)
12.40 -- 12.55 : 15 minutes discussion
What does it mean to say that there are two systems?
In one domain there are two (or more) processes with potentially conflicting outputs.
minimal illustration
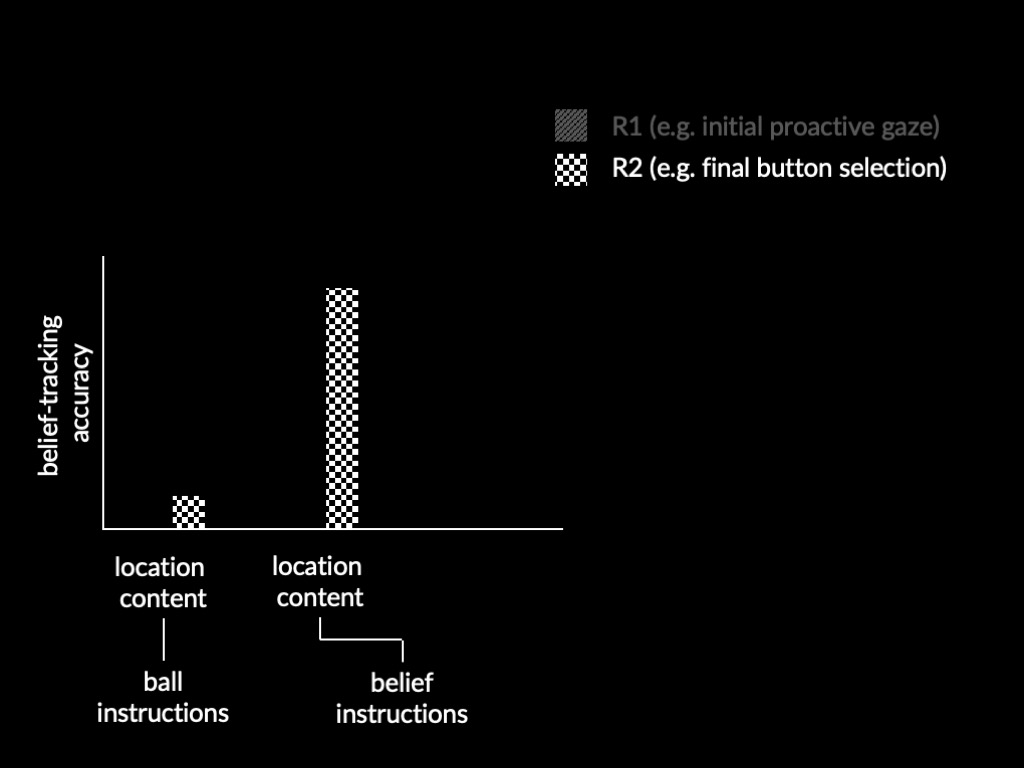
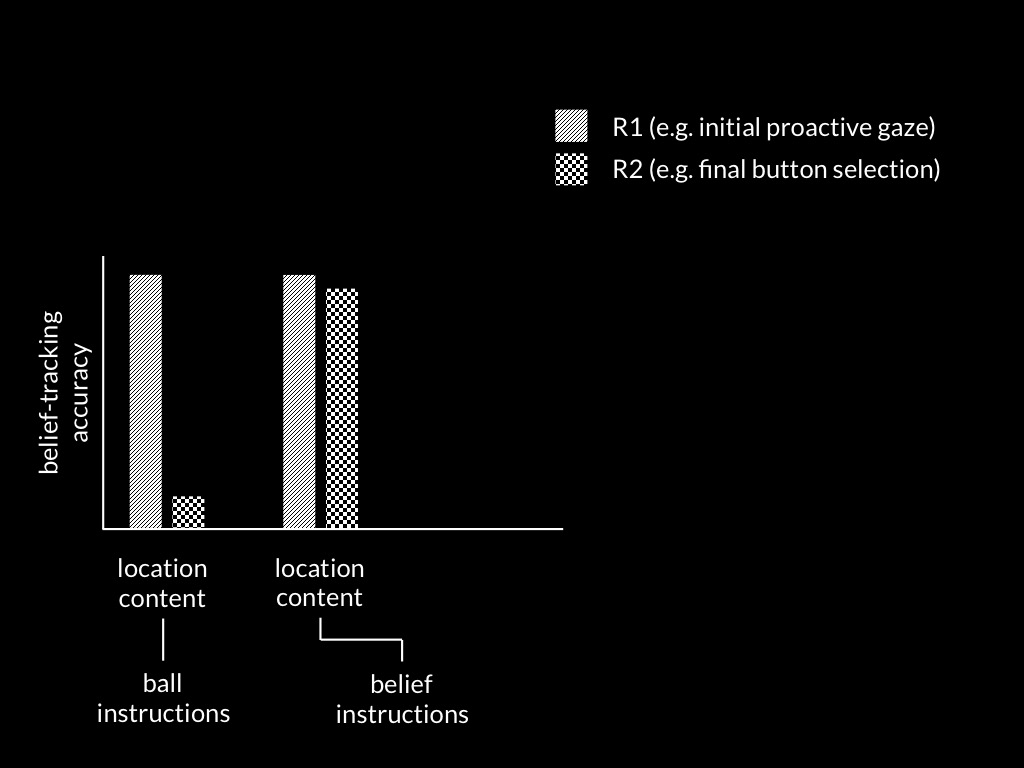
What do you compute that enables you to track toxicity?
Option 2 (slow but accurate) : measure molecular composition (feed it to shellfish and use liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry)
Option 1 (limted but fast) : experience disgust
‘Disgust [...] originated in [...] a food-rejection impulse or motivation triggered by the ingestion of [...] substances [...] that are bitter. Because many bitter substances are toxic, [..] distaste [...] has a clear [...] adaptive function.
Distaste appears to have very ancient origins: Even sea anemones, which first evolved some 500 million years ago, will expel bitter foods from their gastric cavity’
(Chapman & Anderson, 2013, p. 300)
Two Systems Theory of Toxicity (core part)
Two (or more) processes for tracking toxicity are distinct:
the conditions which influence whether they occur,
and which outputs they generate,
do not completely overlap.
One process makes fewer demands on scarce cognitive resources than the other.
(Terminology: fast vs slow)

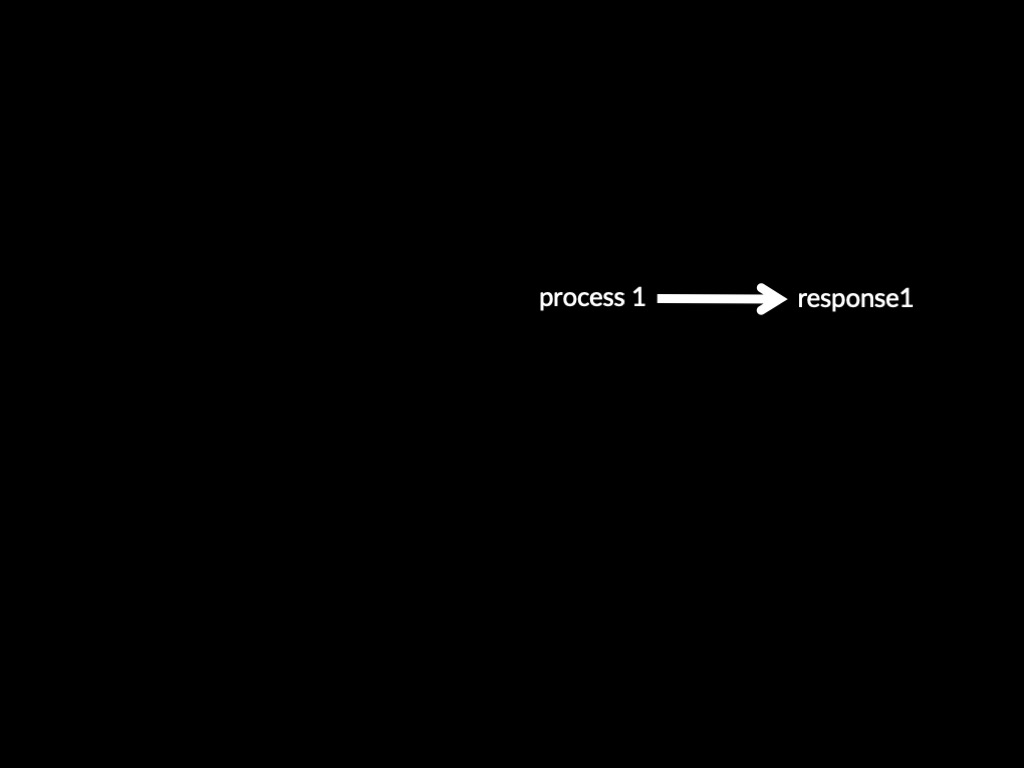
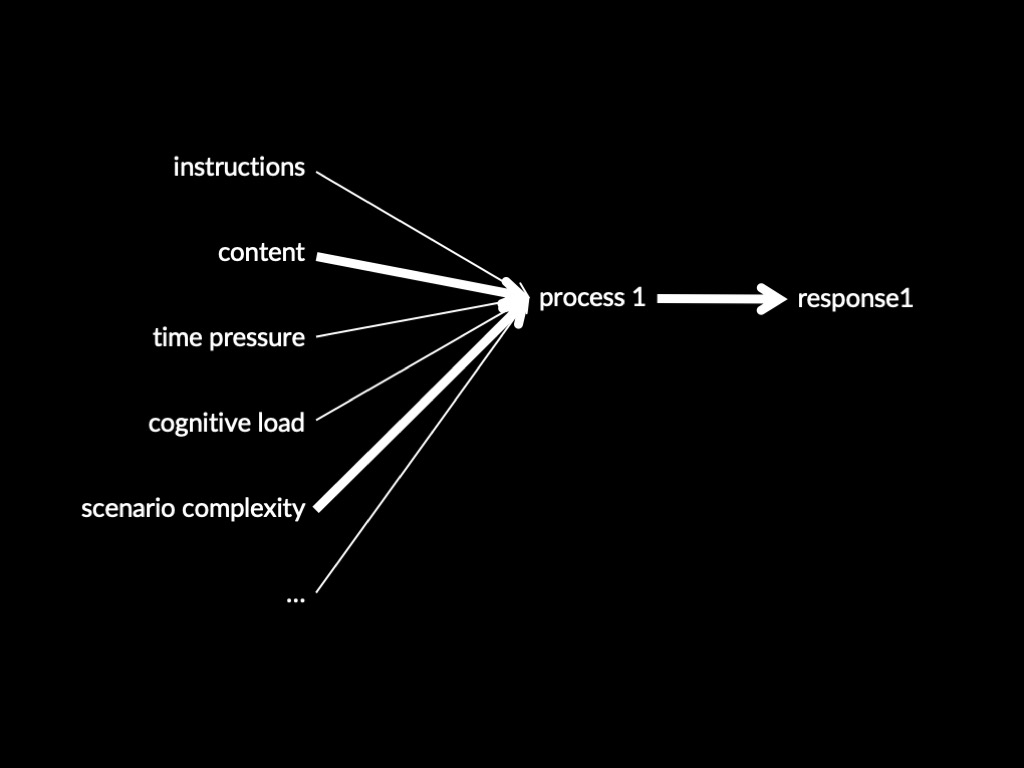
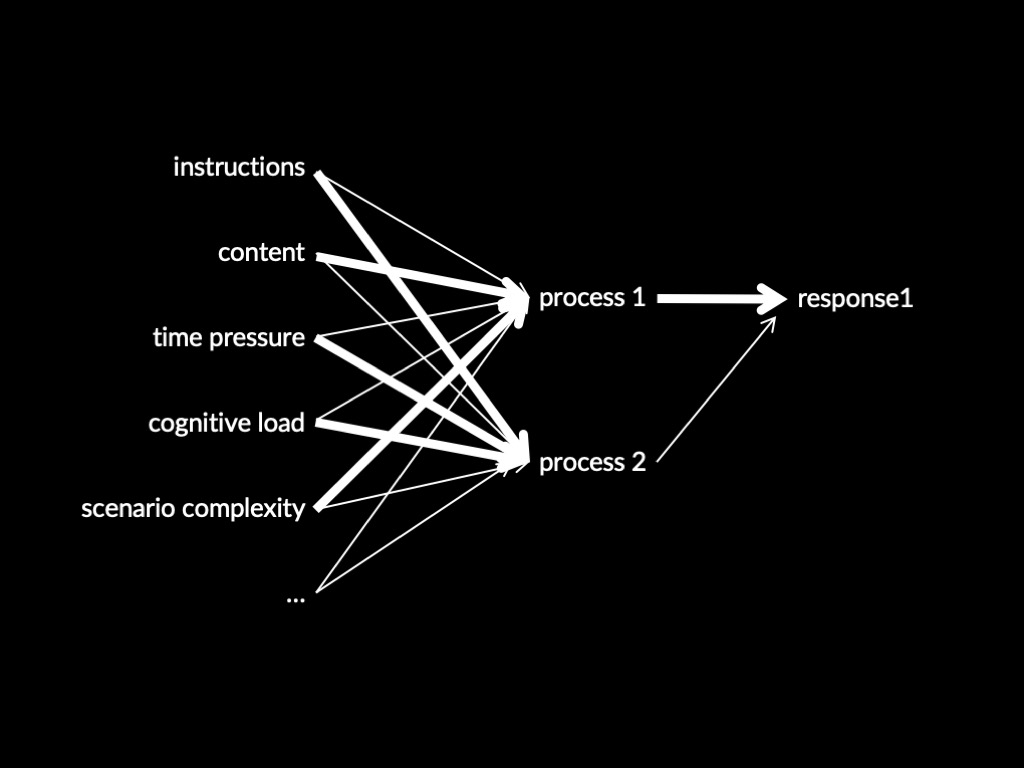
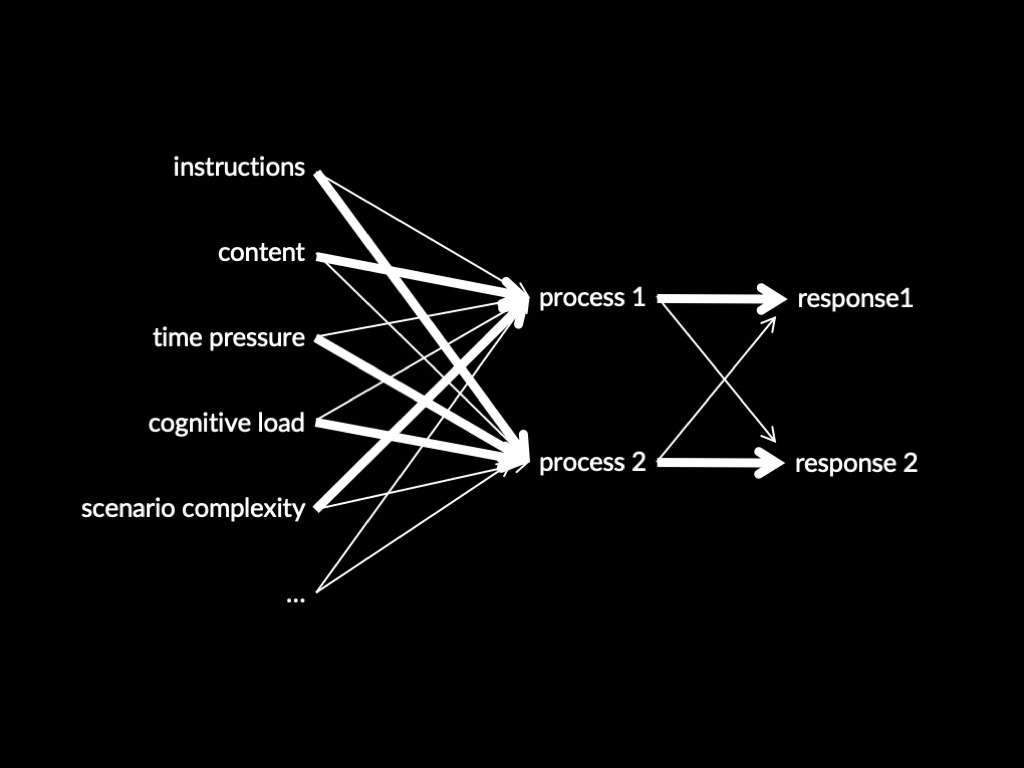
Two Systems Theory of X (core part)
Two (or more) processes concerning X are distinct:
the conditions which influence whether they occur,
and which outputs they generate,
do not completely overlap.
One process makes fewer demands on scarce cognitive resources than the other.
(Terminology: fast vs slow)

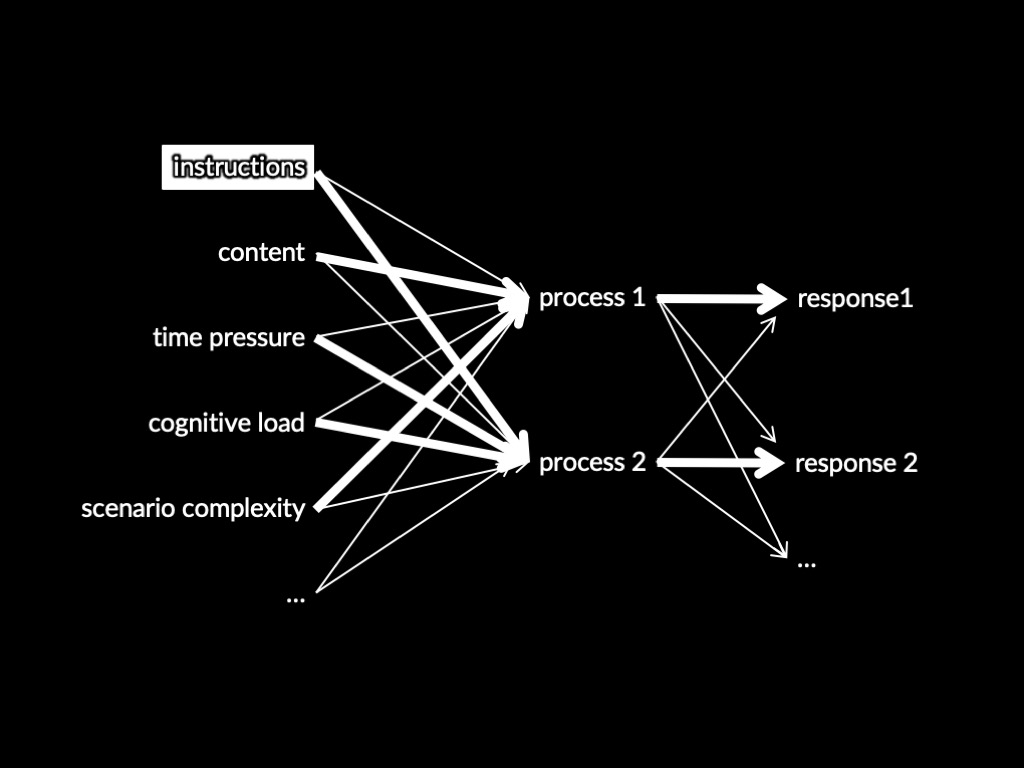






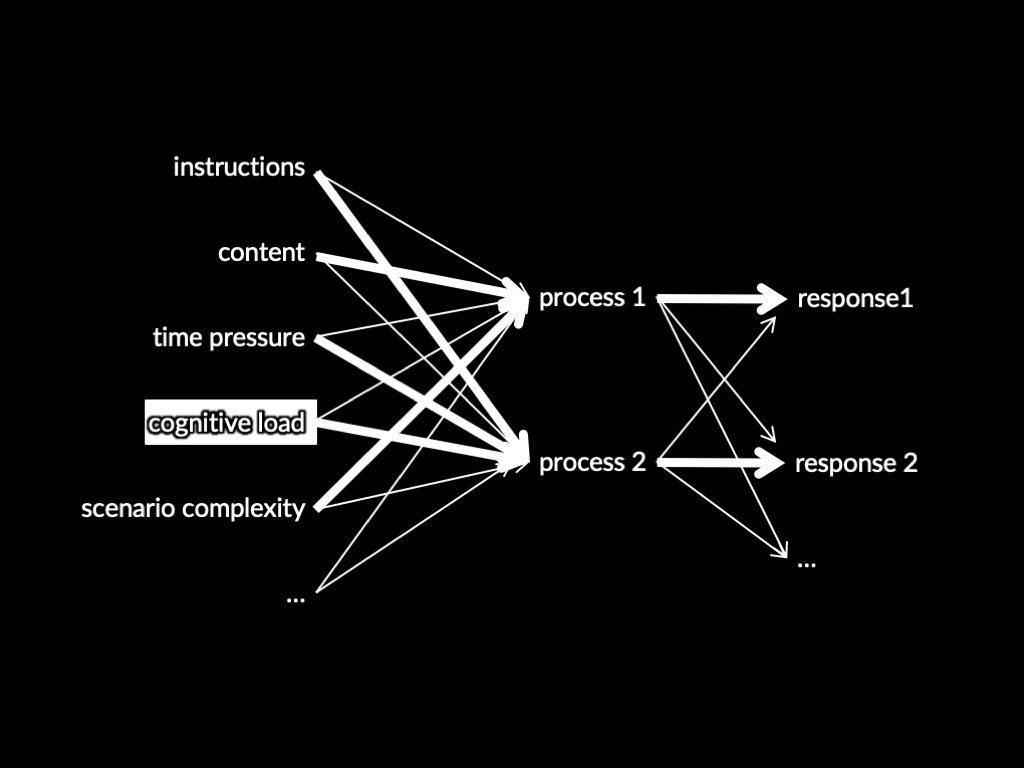

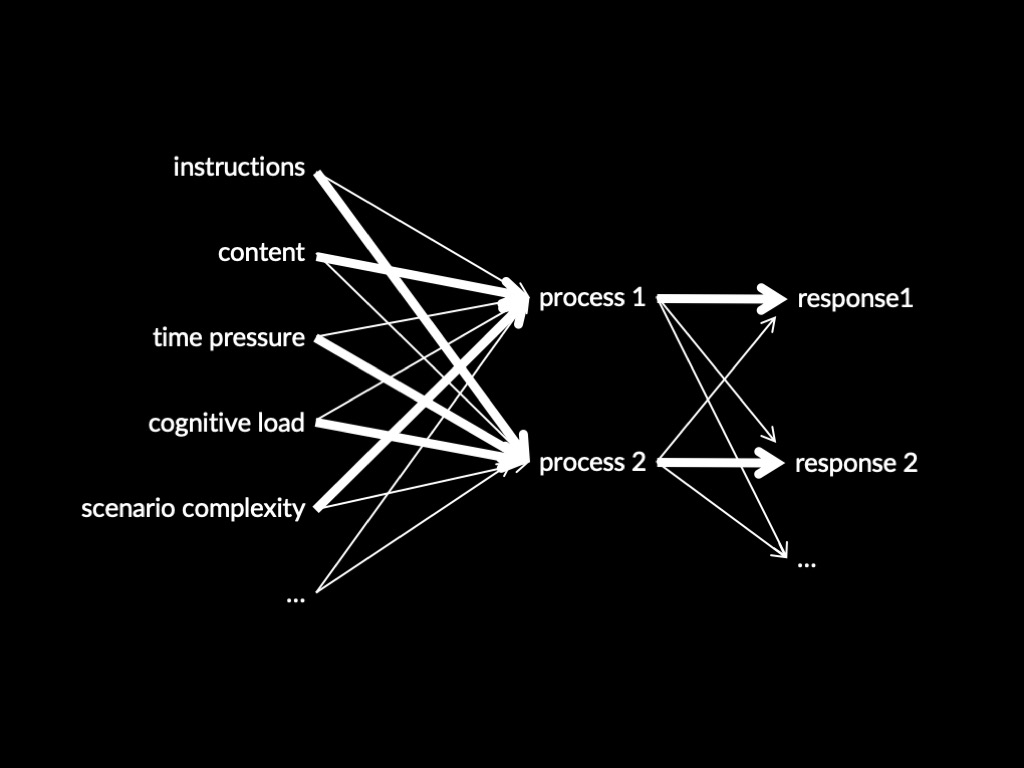
Process 1 -> Response 1
Process 2 -> Response 2


Two Systems Theory of X (core part)
Two (or more) processes concerning X are distinct:
the conditions which influence whether they occur,
and which outputs they generate,
do not completely overlap.
One process makes fewer demands on scarce cognitive resources than the other.
(Terminology: fast vs slow)
Two Systems or Dual Process?
‘We use the term “system” only as a label for collections of cognitive processes that can be distinguished by their speed, their controllability, and the contents on which they operate’ (Kahneman & Frederick, 2005, p. 267).
domains
- reasoning and inference (Evans, 2003)
- judgement and decision-making (Kahneman, 2002)
- memory (Jacoby, 1991)
- social cognition (Gawronski et al., 2014)
- mindreading (Apperly & Butterfill, 2009)
- number (Feigenson, Dehaene, & Spelke, 2004)
- ethics (Greene, Nystrom, Engell, Darley, & Cohen, 2004)
- instrumental behaviour (Dickinson & Pérez, 2018)
- learning (Dayan & Berridge, 2014)
- ? social norms (Bicchieri, 2016)
- ? physical cognition (Kozhevnikov & Hegarty, 2001)
- ? categorical colour (Gilbert, Regier, & Ivry, 2006)
- ? vision (Goodale & Milner, 1992)
- ? agency (Sidarus, Vuorre, & Haggard, 2017)
the questions
In which domains is there substantial evidence for a two systems theory?
And what are the best objections?
How are the two systems distinguished?
What, if any, kind of unity is there across domains?
Why are there two systems?
When, if ever, are two systems better than one?
How, if at all, do the two systems interact? What are the barriers to interaction between them?

Two Systems Theory of X (core part)
Two (or more) processes concerning X are distinct:
the conditions which influence whether they occur,
and which outputs they generate,
do not completely overlap.
One process makes fewer demands on scarce cognitive resources than the other.
(Terminology: fast vs slow)
notes on our web page
http://two-systems.sinigaglia.and.butterfill.com/