Click here and press the right key for the next slide.
(This may not work on mobile or ipad. You can try using chrome or firefox, but even that may fail. Sorry.)
also ...
Press the left key to go backwards (or swipe right)
Press n to toggle whether notes are shown (or add '?notes' to the url before the #)
Press m or double tap to slide thumbnails (menu)
Press ? at any time to show the keyboard shortcuts
Metacognitive Feelings: How Do Fast and Slow Processes Interact?

Metacognitive Feelings: How Do Fast and Slow Processes Interact?
s.butterfill@warwick.ac.uk & c.sinigaglia
How do fast processes influence slow processes?
physical cognition ...
fast process
-> representational momentum
-> phenomenology of experience
-> thinking about experience
-> explicit verbal judgement
phenomenology connects fast and slow indirectly, leaving room for discretion.
‘metacognitive feelings ... allow a transition from the implicit-automatic mode to the explicit-controlled mode of operation.’
Koriat, 2000 p. 150
Two Systems for
Familiarity?
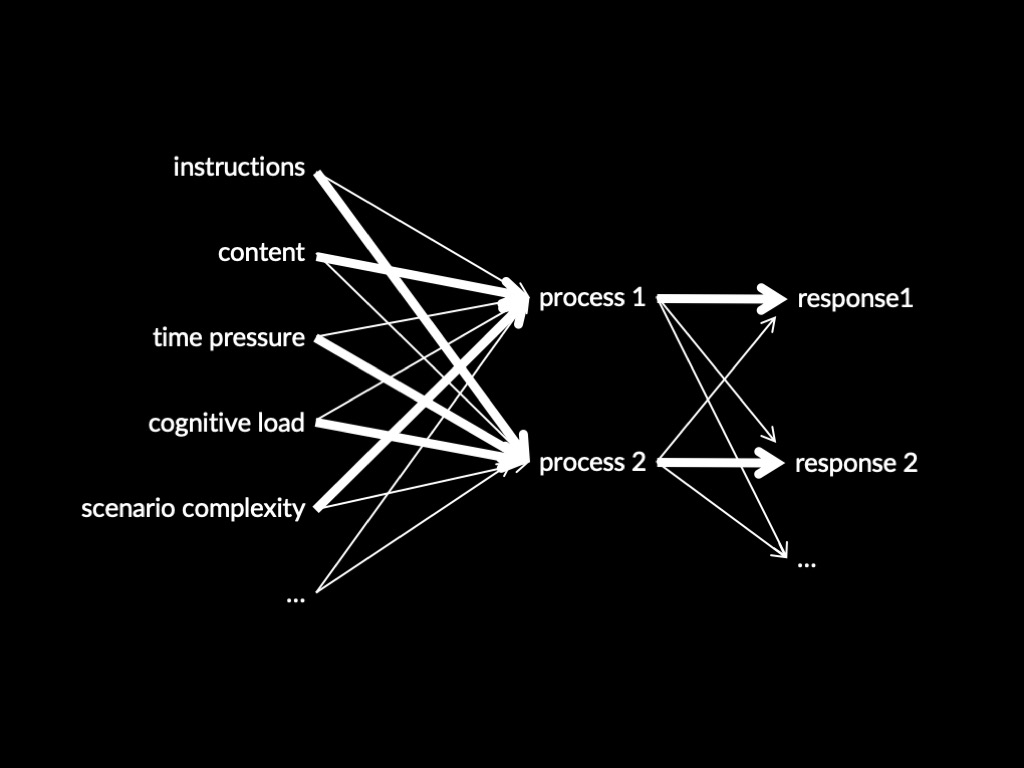

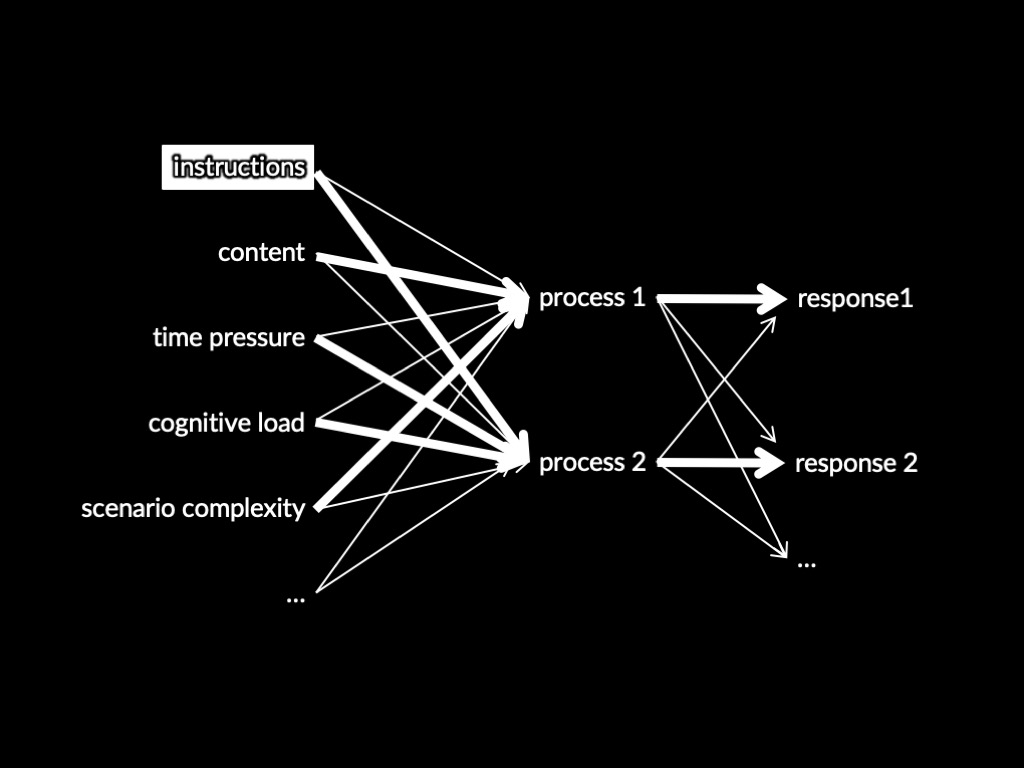

How does the feeling of familiarity enable judgements of familiarity?
processing is fluent
-> metacognitive process detects fluency
-> feeling of familiarity
-> learned association with familiarity
-> judgement
‘metacognitive feelings ... allow a transition from the implicit-automatic mode to the explicit-controlled mode of operation.’
Koriat, 2000 p. 150
beyond familiarity?
What do adult humans compute that enables their unreflective judgements to track inaccessible attributes (such as risk)?
| device | What is tracked? | What is computed? |
| poison detector | toxicity | how encountering it makes me feel |
| risk intuition | probability of death | feeling of dread |
What do adult humans compute that enables their unreflective judgements to track inaccessible attributes (such as risk)?
Affect Heuristic
The more dread you feel when imagining it, the more frequent or risky it is.
Availability Heuristic
The easier it is to bring a case of this cancer to mind, the more frequent or risky it is.
Heuristics require a synchronous link between fast and slow proceses.
The link depends on the phenomenology of emotion (e.g. Affect Heuristic) or of metacognition (e.g. Availability Heuristic).
‘metacognitive feelings ... allow a transition from the implicit-automatic mode to the explicit-controlled mode of operation.’
Koriat, 2000 p. 150
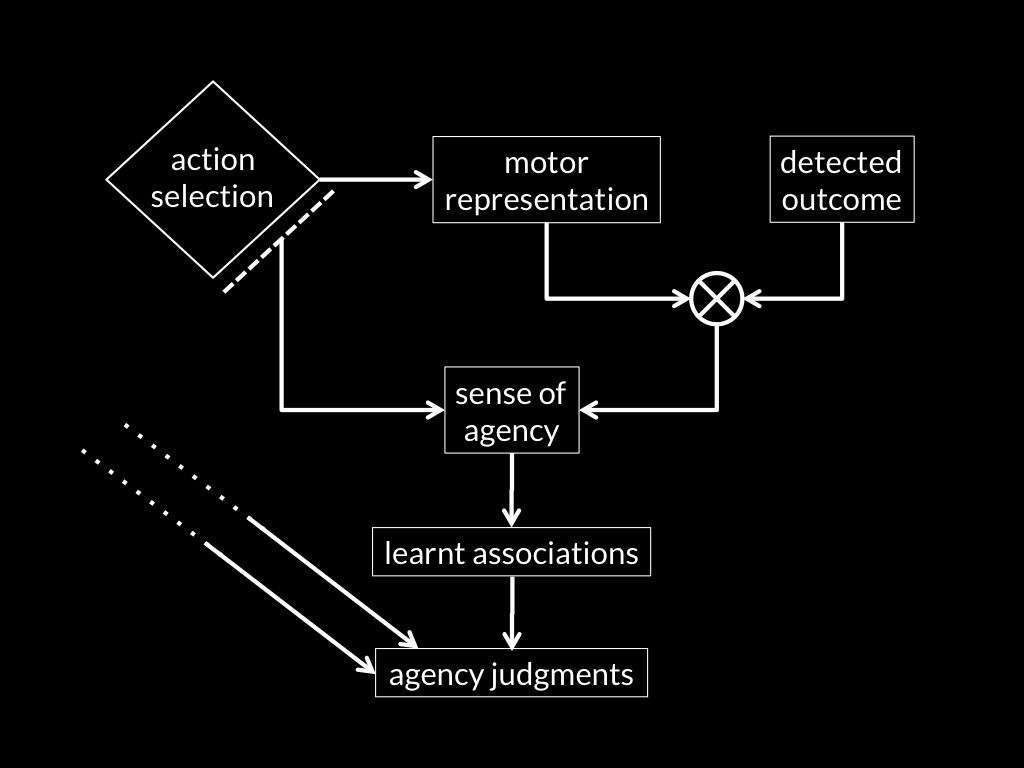
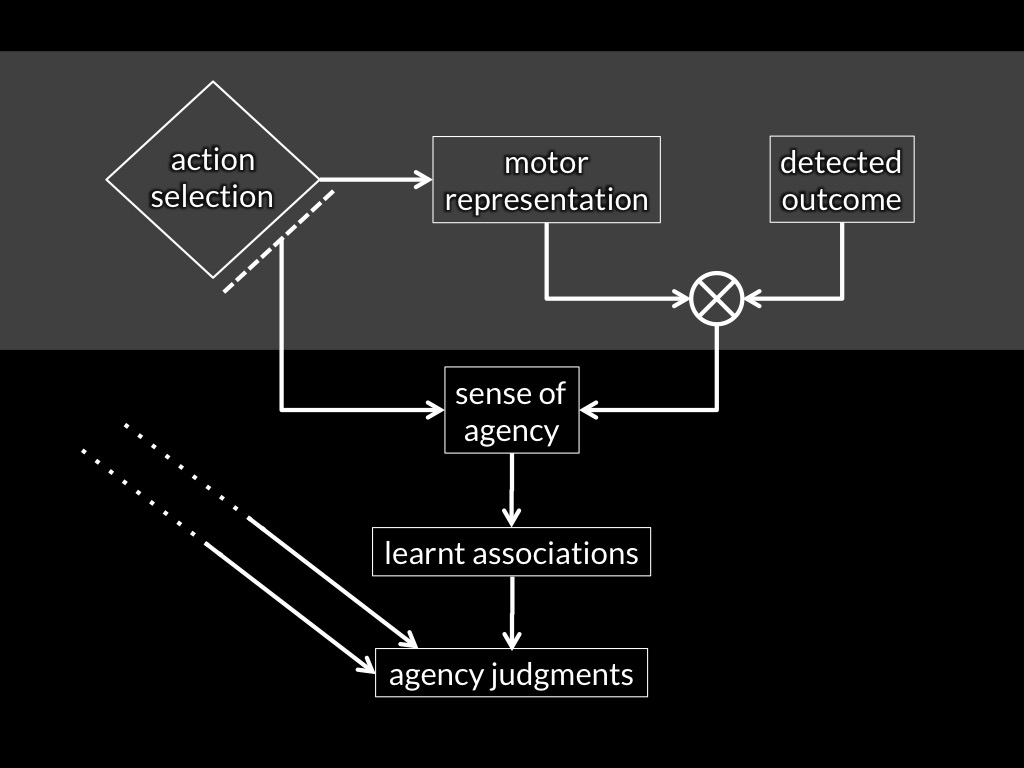
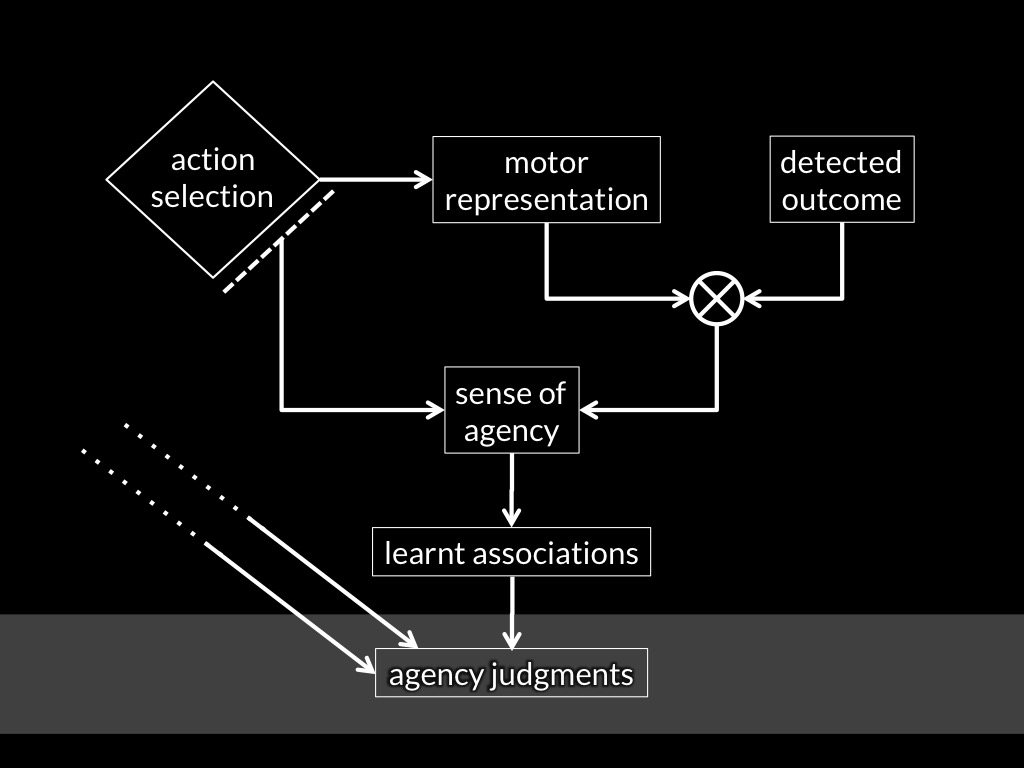
sense of agency

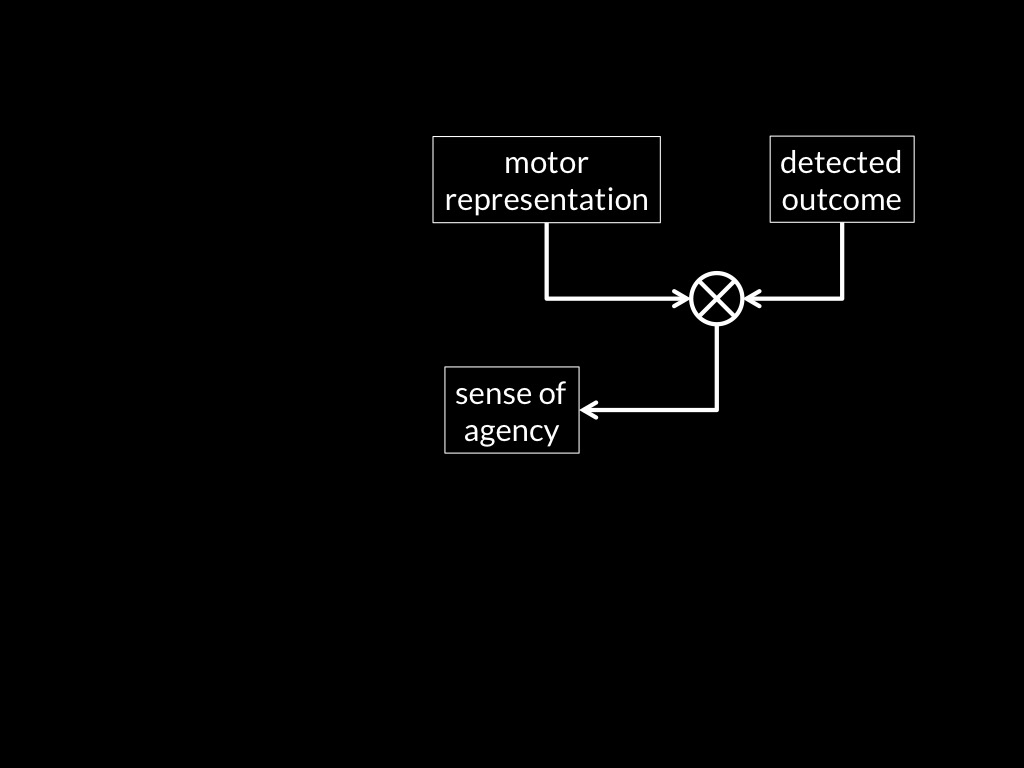
Adapted from Sidarus & Haggard, 2016 figure 5
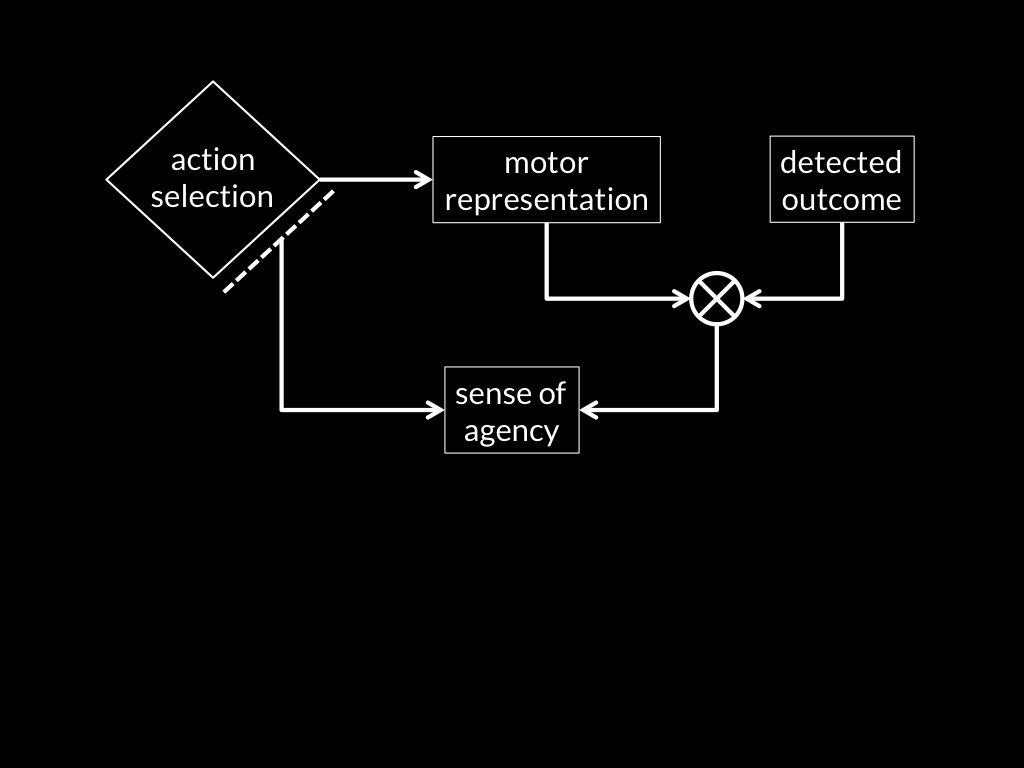
Adapted from Sidarus & Haggard, 2016 figure 5



Metacognitive feelings are intentional isolators.
Intentional isolators prevent inferential integration.
Metacognitive feelings
There are aspects of the overall phenomenal character of experiences which their subjects take to be informative about things that are only distantly related (if at all) to the things that those experiences intentionally relate the subject to.
Metacognitive feelings
can be thought of as
sensations.
Sensations are
- monadic properties of perceptual experiences
- individuated by their normal causes
- (so they do not involve an intentional relation)
- which alter the overall phenomenal character of those experiences
- in ways not determined by the experiences’ contents.
metacognitive feelings trigger beliefs only via associations.

conclusion
How do fast processes influence slow processes?
Could metacognitive feelings explain all influence of fast on slow? --- Mindreading? Ethical cognition? Availability heuristic?
other interfaces linking from fast to slow processes:
- emotion
- behaviour
What about the influence of slow processes on fast processes?